若以直角坐标系的原点为极点,$x$ 轴的非负半轴为极轴建立极坐标系,则线段 $y=1-x\left(0 \leqslant x \leqslant 1\right)$ 的极坐标方程为 \((\qquad)\)
【难度】
【出处】
2014年高考江西卷(理)
【标注】
【答案】
A
【解析】
由极坐标与直角坐标的互化公式带入,整理即可,然后需要注意,在 $0\leqslant x\leqslant 1$ 时,$\theta$ 的取值范围.由极坐标与直角坐标的互化公式得直线 $y=1-x$ 的极坐标方程为\[\rho\sin \theta=1-\cos \theta,\]即 $\rho = \dfrac{1}{\cos \theta + \sin \theta} $.
在直角坐标系画出原线段的图象: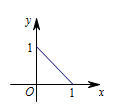 所以其对应的极坐标方程中极角的范围是 $\left[ 0 ,\dfrac{{\mathrm{\mathrm \pi} }}{2}\right]$.
所以其对应的极坐标方程中极角的范围是 $\left[ 0 ,\dfrac{{\mathrm{\mathrm \pi} }}{2}\right]$.
综上,线段 $y=1-x\left(0 \leqslant x \leqslant 1\right)$ 的极坐标方程为 $\rho = \dfrac{1}{\cos \theta + \sin \theta} $,$ 0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{{\mathrm{\mathrm \pi} }}{2}$.
在直角坐标系画出原线段的图象:
 所以其对应的极坐标方程中极角的范围是 $\left[ 0 ,\dfrac{{\mathrm{\mathrm \pi} }}{2}\right]$.
所以其对应的极坐标方程中极角的范围是 $\left[ 0 ,\dfrac{{\mathrm{\mathrm \pi} }}{2}\right]$.综上,线段 $y=1-x\left(0 \leqslant x \leqslant 1\right)$ 的极坐标方程为 $\rho = \dfrac{1}{\cos \theta + \sin \theta} $,$ 0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{{\mathrm{\mathrm \pi} }}{2}$.
题目
答案
解析
备注