已知函数 $f\left( x \right)$ 是定义在 ${\mathbb{R}}$ 上的奇函数,当 $x \geqslant 0$ 时,$$f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left({\left|{x-{a^2}}\right| + \left|{x-2{a^2}}\right|-3{a^2}}\right).$$若 $\forall x \in{\mathbb{R}}$,$f\left({x-1}\right) \leqslant f\left( x \right)$,则实数 $a$ 的取值范围为 .
【难度】
【出处】
无
【标注】
【答案】
$\left[{-\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6},\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6}}\right]$
【解析】
当 $a\neq 0$ 时,用分界点 $x=a^2$ 和 $x=2a^2$ 讨论,结合函数的奇偶性,不难画出函数的草图如图.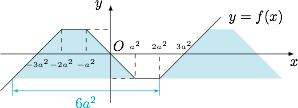 题中条件“$\forall x\in{\bf R},f(x-1)\leqslant f(x)$”的含义是将函数图象向右平移 $1$ 个单位,设法将图象中的“山”(阴影部分)移动到原图象的下方(可以与边界重合).因此有 $6a^2\leqslant 1$.结合 $a=0$ 时显然符合题意,可解得实数 $a$ 的取值范围是 $\left[{-\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6},\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6}}\right]$.
题中条件“$\forall x\in{\bf R},f(x-1)\leqslant f(x)$”的含义是将函数图象向右平移 $1$ 个单位,设法将图象中的“山”(阴影部分)移动到原图象的下方(可以与边界重合).因此有 $6a^2\leqslant 1$.结合 $a=0$ 时显然符合题意,可解得实数 $a$ 的取值范围是 $\left[{-\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6},\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6}}\right]$.
 题中条件“$\forall x\in{\bf R},f(x-1)\leqslant f(x)$”的含义是将函数图象向右平移 $1$ 个单位,设法将图象中的“山”(阴影部分)移动到原图象的下方(可以与边界重合).因此有 $6a^2\leqslant 1$.结合 $a=0$ 时显然符合题意,可解得实数 $a$ 的取值范围是 $\left[{-\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6},\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6}}\right]$.
题中条件“$\forall x\in{\bf R},f(x-1)\leqslant f(x)$”的含义是将函数图象向右平移 $1$ 个单位,设法将图象中的“山”(阴影部分)移动到原图象的下方(可以与边界重合).因此有 $6a^2\leqslant 1$.结合 $a=0$ 时显然符合题意,可解得实数 $a$ 的取值范围是 $\left[{-\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6},\dfrac{\sqrt 6}{6}}\right]$.
题目
答案
解析
备注